Real-time monitoring of transactional data for AI-driven banks
The pervasive use of AI agents in the banking ecosystems poses new risks to banks as for example financial losses by erroneous algorithms, compliance violations by incorrect transactions, data integrity issues, operational disruptions, reputational damage and legal & regulatory consequences.
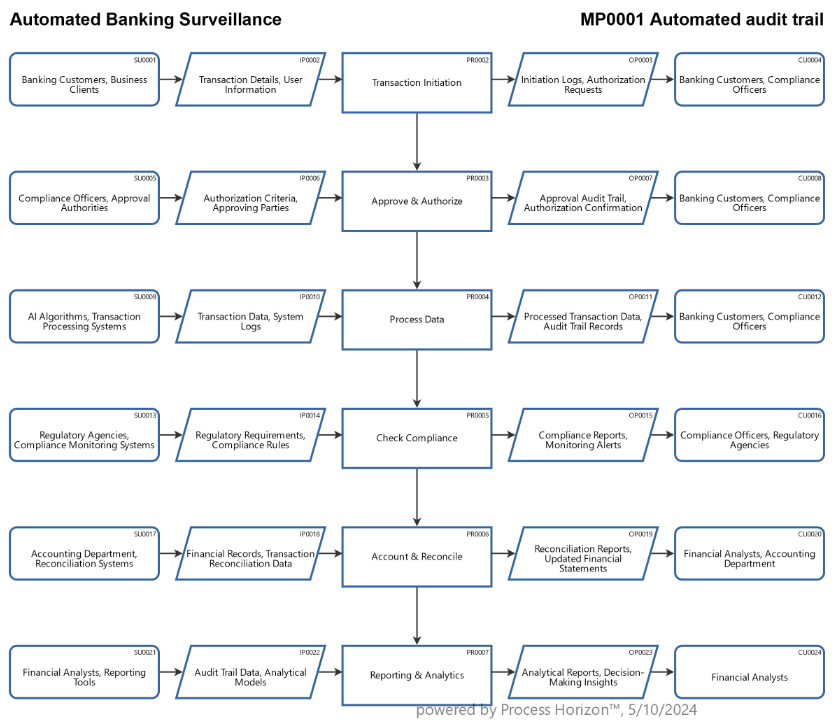
To prevent errors compounding in a short time, ongoing automated monitoring and oversight of AI-driven transaction processing should be implemented as a common data base for auditors and regulators.
To be able to identify irregular transactions at origin, ongoing monitoring by automated audit trails of all transactional data in real time are needed and be made available to internal and external auditors as well as to regulators for auditing by their proper AI auditing agents.
Audit trail from source to destination (accounting):
Who
- Identification: Details of the individuals or entities involved in the transaction, including names, user IDs or unique identifiers.
- Roles: Description of the roles or positions of key stakeholders, such as the sender, recipient, approving authority or system administrator.
What
- Transaction Details: Specifics of the transaction, including the amount transferred, type of transaction (e.g., money transfer, purchase) and any accompanying notes or comments.
- Action Taken: Description of the action taken in the transaction, such as an authorization, approval or rejection.
Where
- Location: Information on the location or source of the transaction, which could include the physical location of the user, the IP address or the platform used for the transaction.
When
- Timestamp: Date and time when the transaction occurred, indicating the exact moment the transaction was initiated, approved and completed.
- Chronological Order: Sequence of events in the transaction process, documenting the timeline of actions taken.
How
- Method: Description of the method used to execute the transaction, whether through an online platform, mobile application, in-person interaction or automated process.
- Authorization Process: Details on how the transaction was authorized, including authentication methods, approval workflows and any code or authorization token generated.
Why
- Purpose: Explanation of the purpose or reason behind the transaction, such as a business payment, personal transfer or client request.
- Justification: Rationale for the transaction, indicating why it was necessary, valid and compliant with policies and procedures.
An AI-based automated end-to-end audit trail from transaction initiation to accounting can provide a detailed record of the transaction lifecycle in a process context, incorporating artificial intelligence to enhance efficiency, accuracy and transparency.
Full transparency of transactional data is needed for real-time detection of unusual or suspicious activities as well as proactive risk mitigation, compliance with regulations, pattern recognition to flag abnormal transactions and safeguarding customer trust.
Using the following link you can access this sandbox process model in the ProcessHorizon web app and adapt it to your needs (easy customizing) and export or print the automagically created visual process map as a PDF document or share it with your peers: https://app.processhorizon.com/enterprises/JGvjVebZ4vqmb8v8htefKToX/frontend

