AI-Driven QbD in Healthcare Services
Quality by Design is a systematic approach to development that begins with predefined objectives and emphasizes product & services as well as process understanding and process control, based on sound science and quality risk management.
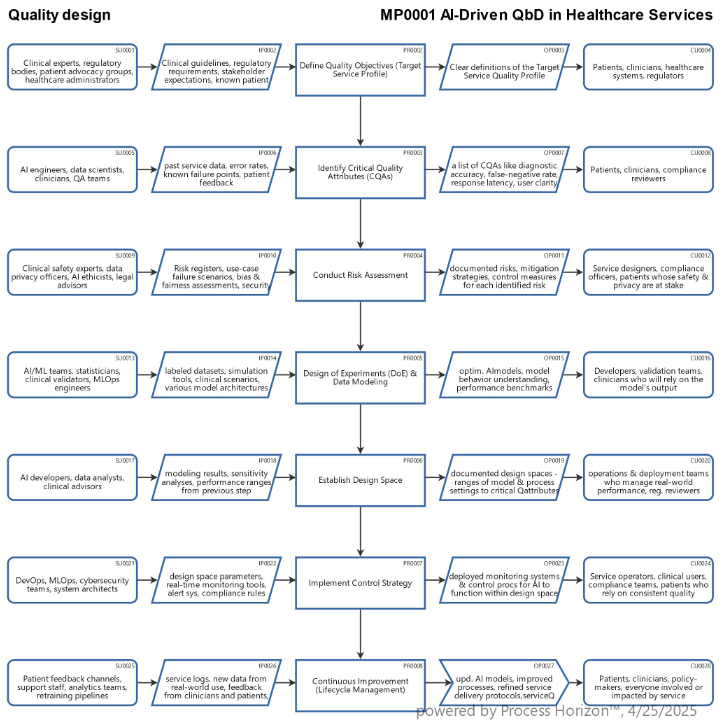
The process and methodology of Quality by Design (QbD) applied to products or services follows a structured, science- and data-driven approach to ensure that quality is built in by design, not just tested later.
1. Define Quality Objectives
- Product: Define the Target Product Profile (TPP) or Target Product Quality Profile (TPQP), i.e. what the product is supposed to do (e.g., therapeutic effect, dosage form).
- Service: Define the Service Quality Goals, i.e. customer satisfaction, timeliness, reliability, compliance.
2. Identify Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)
- Determine which measurable attributes must be controlled to ensure quality:
- Product: purity, potency, stability, appearance
- Service: speed, accuracy, customer satisfaction, resolution time
3. Conduct Risk Assessment
- Use tools like FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) or Ishikawa (fishbone) diagrams to identify:
- What could go wrong?
- How likely is it?
- What impact would it have on quality?
4. Design of Experiments (DoE)
- Systematically test different inputs and conditions to understand:
- Which process parameters affect CQAs?
- How do variables interact?
- What is the optimal range for each input?
5. Establish a Design Space
- Define a multi-dimensional combination of input variables (materials, settings, conditions) that yield a product/service meeting quality standards.
- Operating inside the design space is considered safe.
- Changes outside it require regulatory re-evaluation (for pharma).
6. Develop a Control Strategy
- Decide how to monitor and control critical variables:
- Use real-time monitoring e.g. Process Analytical Technology - PAT)
- Set control limits and action plans for deviations
7. Continuous Improvement (Lifecycle Management)
- Use data analytics, machine learning, or statistical process control (SPC) to refine and optimize.
- Adapt the process based on real-world performance & customer feedback.
This end-to-end QbD methodology ensures that AI in healthcare services is not only effective but also reliable, transparent and aligned with patient safety & regulatory expectations.
Using the following link you can access this sandbox SIPOC model in the ProcessHorizon web app and adapt it to your needs (easy customizing) and export or print the automagically created visual AllinOne SIPOC map as a PDF document or share it with your peers: https://app.processhorizon.com/enterprises/dWkcYqRtwAgwXjvXCHbUxBH8/frontend

